Views certainly appear polarised on the success of Germany’s energy transition to date. Ambrose Evans-Pritchard writing in The Telegraph certainly believes the dream is over. It would be good to hear from EiD readers about their views. Is it really economic suicide?
Romantic Germany risks economic decline as green dream spoils
Germany is committing slow economic suicide. It has staked its future on heavy industry and manufacturing, yet has no energy policy to back this up.
Instead, the country has a ruinously expensive green dream, priced at €700bn (£590bn) from now until the late 2030s by environment minister Peter Altmaier if costs are slashed – and €1 trillion if they are not. The Germans are surely the most romantic nation on earth.
The full implications of this may become clear over the next decade, just as Germany’s ageing crisis hits with maximum force and its engineers retire; and just as German voters discover – what they suspect already – that it costs real money to hold a half-baked euro together.
The likelihood is that Germany will start to lose its economic halo soon, “de-rated” like others before it.
America was over-rated in 2000. Russia and Britain were over-rated in 2007. Brazil, India and a string of mini-BRICS were over-rated in 2011. Today the country most obviously trading at its cyclical peak is Germany, a geostrategic “short” candidate that is drawing down its credit from past efforts. However, the slippage may be slow, since Germany has locked in a lasting edge over southern Europe through a fixed exchange rate.
Chancellor Angela Merkel tied a deadweight around the ankles of her country when she suddenly – and flippantly – abandoned her nuclear policy after Japan’s Fukushima disaster in 2011. “This has forever changed the way we define risk,” she said at the time. “It’s over.”
She was talking about politics, of course, not science. It was an earthquake and tsunami that caused the Fukushima tragedy. Germany’s nuclear plants are not at risk from such flooding, nor are they built on tectonic faultlines. As a scientist with a PhD in subatomic reactions, Dr Merkel knows that the post-Fukushima panic in Germany was hysterical.
Eight nuclear reactors were shut immediately, the rest to be wound down by 2022. This will cut off a fifth of Germany’s total power. To global astonishment – and the Left’s chagrin – she then unveiled her Faustian “Energiewende”, the grand plan to derive half of all German electricity from wind, solar, biomass and other renewables by 2035, and 80pc by the middle of the century.
The assumption was that Germany would gain a “first-mover” lead in renewables, reaping the reward later. They overlooked the Chinese, who copied the technology. Chinese firms gouged the German home market with the aid of cheap labour, a cheap yuan, cheap state credit and a global trade system that let them get away with it.
The German solar industry has been smashed. QCells, Conergy, Solon and Solarworld have all gone bust or faced debt restructuring. The subsidies for feed-in tariffs have been leaked abroad. Eight of the world’s 10 biggest solar firms are now Chinese.
As a solar enthusiast, I am grateful to the Germans for their altruism. Roughly €100bn of their money has gone up in smoke – one way or another – developing solar technologies that have helped drive down costs to near “grid parity” in low latitudes. The great prize of market-based solar is within grasp. Sadly for German citizens, they will see no special benefit.
In the end, it is wind from thousands of turbines in the Baltic – generating 25,000 megawatts (MW) by 2030 – that is supposed to power Europe’s industrial heart. This is an astounding gamble. As of today, barely 300 megawatts of offshore wind capacity is in place. The cables across the country do not exist.
Utilities are turning to coal – and cheap lignite, emitting 30pc more CO2 – to plug the gap. Germany’s greenhouse emissions rose 1.6pc last year. In the US they fell to a 20-year low thanks to the switch from coal to shale gas. Sudden surges of power – the intermittency effect – are overloading the grid and crippling utilities E.ON and RWE. The pair have threatened to shut down 21,000MW of power plants.
The Chemical Industry Federation has called for an immediate freeze in costs before its members are priced out of the global market. “Spiralling energy costs will soon drive us to the wall. It has become dangerous, and any further rise will break the back of small and medium firms,” it said.
Electricity prices are twice as high as in America. Natural gas costs are four times as high, forcing the chemical giants of the Ruhr and the Rhine to decamp across the Atlantic. BASF is building its new site for emulsion polymers in Texas, the latest of a €4.2bn investment blitz in the US.
Günther Oettinger, Germany’s EU commissioner, has called for a top-to-bottom review of the policy and a dash for shale. “We need industry; we cannot be the good guys for the whole world if no one is follows suit,” he said.
This should be the galvanizing issue in Germany’s election campaign. It was hardly mentioned in Dr Merkel’s recent soporific debate with Social Democrat leader Peer Steinbruck, eclipsed by a clash on Autobahn speed limits.
Mr Steinbruck called the Energiewende a “disaster”, but only because it has been mismanaged. “I have nothing against the idea,” he said.
It is certainly a dog’s dinner, even if the origins go back to a 20-year guarantee for subsidies issued by the SPD-Green coalition in 2000. This is paid for though a fund levied on all electricity users.
At the time, Green leader Jurgen Trittin said it would cost consumers no more than a “scoop of ice cream”. As a false prospectus, that surely rivals the line by Bavaria’s leader in the early 1990s: that the risk of Germany ever having to bail out a future eurozone partner was less than the risk of “famine in Bavaria”.
The levy has been rising exponentially, up 47pc this year alone. This is added to the bills of consumers. Households are paying ever more because a growing army of “energy-intensive” industries and firms competing in the global market are exempt.
The assumption long ago was that global energy costs would ratchet up, making the levy unneccesary. The Merkel government was caught off-guard by the US shale gas revolution, though the writing has been on the wall since 2009.
The levy policy is turning into a nexus of distortions – “Madness”, as the Handlesblatt screamed on its front page – since firms that have slashed energy use the most are penalised. One has taken a case to the top court. The burden on households is politically toxic. Property owners enjoy a solar income. Renters suffer the extra levy. The poor subsidise the rich. Besides, experts say it is only a matter time before the vice tightens on industry as well.
Stephan Kohler, from the state-funded German Energy Agency, says the system is out of control. He has called for the offending energy law to be “abolished”. Is anybody listening?
Angela Merkel says she is “more convinced than ever” that her green gamble will pay off. “If anyone can manage it, it’ll be the Germans. It’s not easy, but we can do it.”
Famous last words.

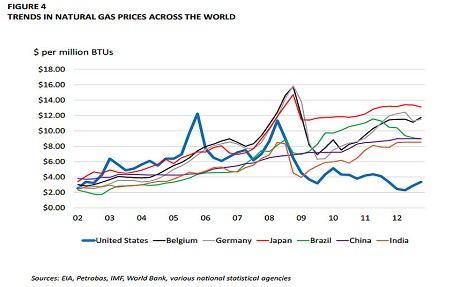
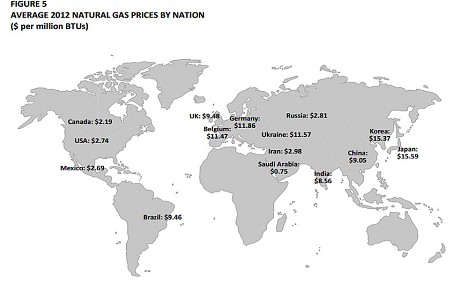
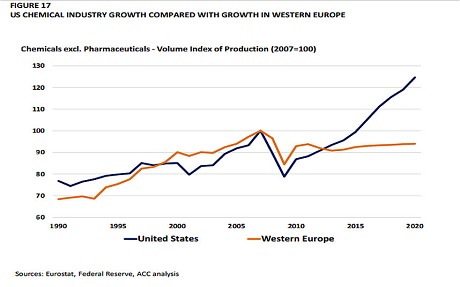
The reality is that the German economy is booming with renewables approaching 25% share of electricity generation. In Britain it is less than 10% and the economy is just about to recover. The cost figures are not realistic – where do those come from? Read the views from Germany’s most respected energy economist here: http://www.claudiakemfert.de/fileadmin/user_upload/pdf/European_Energy_Review.pdf
Jan, thank you so much for this. This really helps.
The Telegraph article is written by someone with the all-too familiar blinkered “renewables glass half-empty” mentality that is so depressingly prevalent in the British media, among British politicians at all levels and indeed among British engineers. In contrast, German engineers seem to be at the centre of discussions about ‘how’ the energy transition is to be done, rather than explaining that it is all too difficult. As for Germany suddenly abandoning nuclear after Fukushima, this is nonsense. The German nuclear exit strategy had been agreed long before Fukushima. All that happened after Fukushima was that the nuclear exit strategy went back to its originally agreed timescale (the Merkel government had previously deviated from that by extending the operating life of some of the existing nuclear plants). A British-style nuclear renaissance pipe dream was never on the agenda in Germany. The sooner plans for new nuclear plants in Britain are abandoned, the better, so that we can start firing on all renewables cylinders. For a better indication of what is happening in Germany than the Telegraph article see the interesting article at http://www.downtoearth.org.in/themes/DTE/germany/germany.htm
Quote: “Will Germany be able to solve all problems and meet challenges that energiewende has thrown up? Can it meet all its targets? I believe, it can and it will. The exciting thing about energiewende is not how much renewable energy Germany has installed so far, but how the German government, businesses and civil society are thinking about the energy transition. I believe the German society has crossed the hump.”
Herbert, Thanks so much for this. So, how do we change the British press on this?
Good question! I suppose it is important that the “renewables glass more than half-full fraternity” keeps beating the drum – see http://herbeppel.blogspot.co.uk/2013/06/minister-wrong-over-windfarms.html for example.
Interestingly, Monday, September 16th, the Financial Times has a similar article on the German situation. See: http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/c5b9815a-1c44-11e3-a8a3-00144feab7de.html#axzz2exoK4b73. It has an interesting quote: Kurt Bock, chief executive of chemical maker BASF, mused that “abroad, people are observing this German experiment with wide eyes and partly with a little Schadenfreude”. There is also another interesting quote: Ulrich Grillo, head of the Federation of German Industries, said: “It was always clear that there would be a price . . . [But] the new energy supply architecture was entered into without an architect, a construction plan or site management.”
The article also mentions how gas plants are being closed and coal plants opened. And also mentions the difficulty of building new transmission lines to take the renewable energy from the north and distributing to the industrial south.
Interesting situation and one for all of us to watch.
Yes, definitely an interesting situation, not least in view of the parliamentary elections in Germany this coming Sunday, the outcome of which will no doubt have some bearing on the future direction of Germany’s energy transition.
Readers may care to google other articles by Ambrose Evans Pritchard; they will find that over many years he has consistently adopted a hostile position to anything a) not British and b) anything remotely ecologically friendly. Might I suggest to the editor that in future he ignores entirely the rants from this xenophobic right wing propagandist, just as any sensible Briton does?
The editor takes note. Thanks for this.